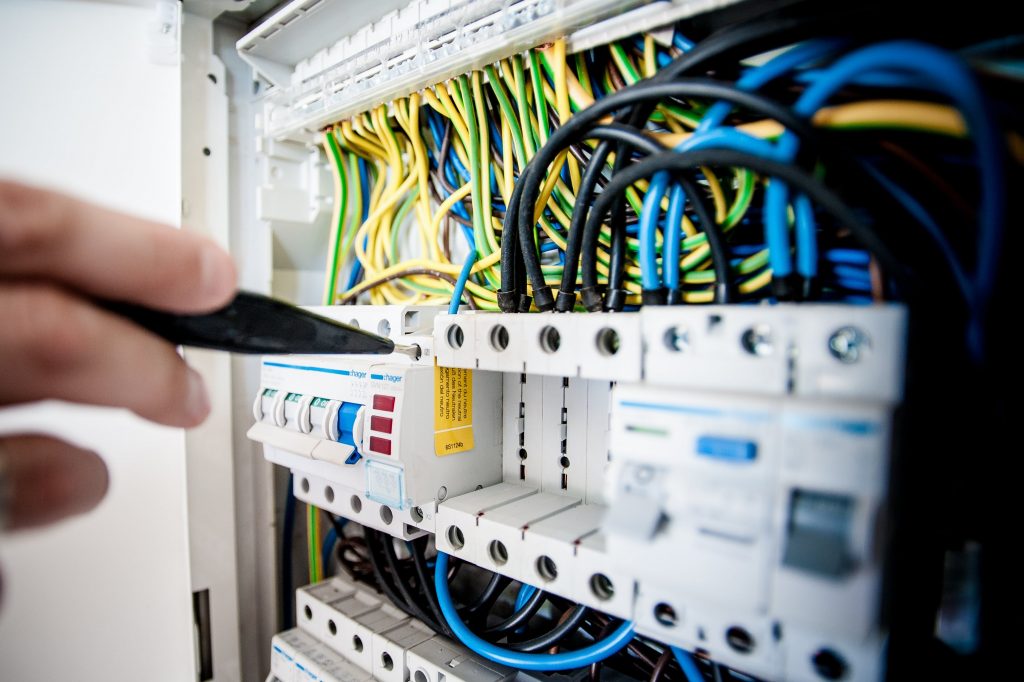
Low-voltage cables, rated at 0.6/1KV or lower, are ubiquitous in our daily lives, playing crucial roles in various settings from industrial applications to residential electrical connections. Their design and composition make them flexible and reliable for safely and efficiently delivering electrical power. Below, we present a comprehensive guide to the characteristics and applications of these essential cables.
Structure of the Cables
Low-voltage conductors consist of three main components: the conductor itself, typically made of intertwined copper or aluminum strands, responsible for carrying electrical current. The insulation surrounding the conductor prevents current leaks and ensures installation safety. Additionally, these cables often feature a protective layer providing mechanical resistance and protection against external factors.
Varieties of Low-Voltage Cables
These cables are available in configurations of single-core, two-core, three-core, and four-core. Single-core cables can be adapted for either single-phase or three-phase lines as required, while two-core cables are ideal for single-phase lines. Three and four-core cables are used in three-phase lines with three and four wires, respectively. Common cross-sectional areas include 10, 16, 25, 35, 50, 70, 95, 120, 150, 185, 240 mm, etc.
Categories of Low-Voltage Cables
These conductors are categorized based on their applications:
Power Cables:
- Used in industrial settings to supply power to large-scale machinery and equipment, ensuring a steady flow of electricity.
General-Use Wires and Cables:
- Primarily employed in domestic electrical connections, data transmission, computer accessories, and consumer electronics, providing reliable electrical power in homes and offices.
Communication Cables:
- Utilized in telecommunications systems, telephony, ticket vending machines, and automatic door control equipment, playing a crucial role in efficient and secure signal and data transmission.
Selection of Low-Voltage Conductors
Choosing the right conductor is crucial to ensure safe and efficient power supply. Considerations include cable materials (aluminum, copper, tinned copper), current load, and structural requirements (shielding, armor). Evaluating installation conditions will help determine additional cable requirements.
Explore Our Low-Voltage CablesMaintenance of Low-Voltage Cables
Proper maintenance is essential to extend their lifespan and ensure reliable operation. Common measures include regular inspections of insulation and protective layers, periodic resistance measurements, and ensuring adequate loading to prevent overheating.
Applications of Low-Voltage Conductors
These conductors are used in diverse fields ranging from indoor power distribution to electric communications, traffic signal control, public transportation power supply, and urban lighting projects, showcasing their versatility.
Advantages of Low-Voltage Conductors
These cables offer several advantages such as low nominal voltage, greater number of cores, simple structure, easy installation, low maintenance costs, and long lifespan, making them a reliable and durable choice for long-term power supply.